The first aid refers to the medical assistance given to someone who has experienced a medical emergency. It’s usually a one-time, short-term treatment that doesn’t involve any equipment or training.
Aims of first aid
There are following 5 main aims of first aid:
1. Preserve life:
While a first aider is someone who holds a first-aid certificate, they are not medical experts. They can do their utmost to ensure that the patient receives basic care and can assist in the treatment of small injuries such as cuts and scrapes that do not require routine or emergency treatment.
However, in life-threatening situations, they focus on saving life until an ambulance arrives, rather than on giving care.
2. Prevent the escalation
The first responders’ efforts are focused on extending the time the patient has until the ambulance comes. The first aider will not stitch the cut if the patient is bleeding heavily, but they will try their utmost to control the bleeding until the ambulance arrives. They will avoid more difficulties and health degradation in this manner.
3. Pain relief
This is only done if it is technically feasible and does not pose a risk to the patient. When a person is bleeding, several pain relievers can be harmful. If you’re not sure if the pain medication you’re taking is right for you, consult a doctor first.
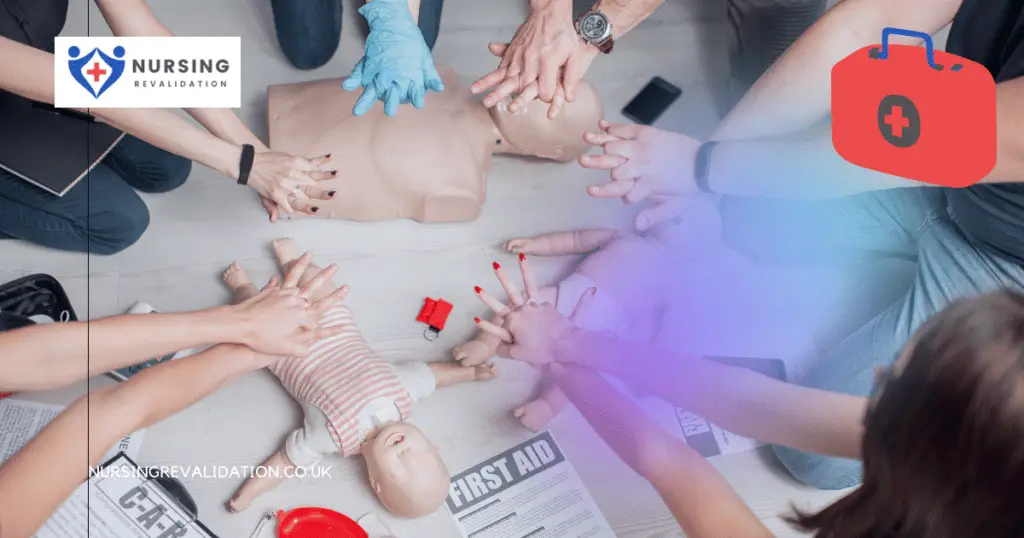 4. Protect the unconscious
4. Protect the unconscious
Protection and safety for both the patient and the first aid provider are crucial considerations when delivering first aid. This also applies to the folks in the immediate vicinity. Protecting the unconscious may entail removing them from a potentially dangerous condition, such as a fire, flooded space, or a busy road.
5. Promote recovery
Protection and safety for both the patient and the first aid provider are crucial considerations when delivering first aid. This also applies to the folks in the immediate vicinity. Protecting the unconscious may entail removing them from a potentially dangerous condition, such as a fire, flooded space, or a busy road.
What are the types of first aid?
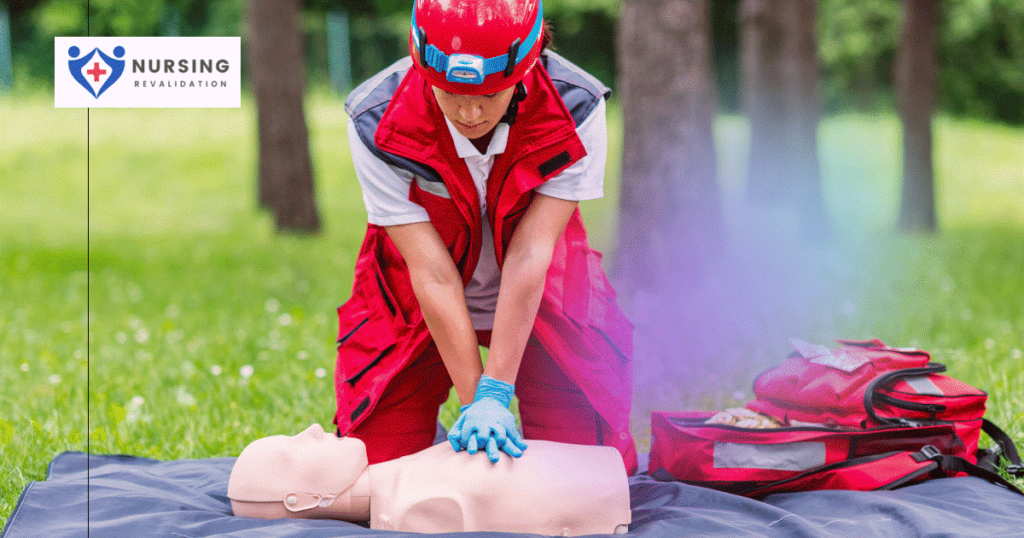
 Emergency First Aid
Emergency First Aid
This includes the content for Basic First Aid involving life threatening injuries. Focus is on Airway, Breathing and Circulatory emergencies and prevention of such. This course comes with CPR A (Adult skills) or CPR C (Adult, Child and Infant skills).
Standard First Aid
The most common course taken. Required by most employers, preferred by parents. All content of the Emergency First Aid is covered as well as wound care, head neck and spine injuries and more. This course comes with CPR A (Adult skills) or CPR C (Adult, Child and Infant skills).
Child Care First Aid This is meant for Day home/Daycare Providers. Covers the content for Standard First Aid plus additional content for Childhood Illnesses and Safety. Comes with a level B CPR (Adult, Child and Infant skills).
Baby Sitter Course
Designed for pre-teens and teens. Basic first aid and safety skills are taught. Focus of this course is preventing and responding to emergencies should they occur while babysitting. This course also offers youth the training to promote themselves as a babysitter to prospective parents.
Home Alone Course
Designed for kids staying home for a short period of time. Focus is on safety and responding to emergencies.
Psychological First Aid
Psychological First Aid is a resiliency building wellness program that equips individuals in supporting themselves and others to cope with the effects of stress, loss, trauma and grief.
The 3 Ps of First Aid
The three Ps of first aid indicate the treatment priorities in first aid.
1. Preserve Life
The first aider’s number one responsibility is to preserve life. This means assessing the emergency scene for dangers to self, as well as to bystanders and, of course, to the casualty.
The caution for potential danger is the first step in the DRSABCD strategy.
stands for
 Danger
Danger- Response
- Send for help
- Airway
- Breathing
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
- Defibrillation
You can download a Basic Life Support chart for this DRSABCD strategy.
2. Prevent Deterioration
This is all about keeping the patient’s condition steady so that it does not deteriorate while waiting for medical help.
The first responder would do this by administering first assistance and providing reassurance. Further injuries would be avoided, and the patient would be placed in a safe and comfortable position
3. Promote Recovery
The first responder’s goal in administering first aid treatment would be to ease discomfort and boost the patient’s confidence. These are crucial steps in assisting with the rehabilitation process.
These three Ps aid in the prioritization of a first responder’s efforts and are crucial in the treatment of victims in an emergency.
What are the 8 main areas of first aid?
The Most Common First Aid Injuries are
- Cut/Scrape: If there is bleeding, press firmly over the site with a clean cloth until it stops, anywhere from three to 15 minutes. …
- Burn
- Insect Bite/Sting
- Splinter
- Sunburn
- Nosebleed
- Sprains, Strains, and Tears
- Fractures
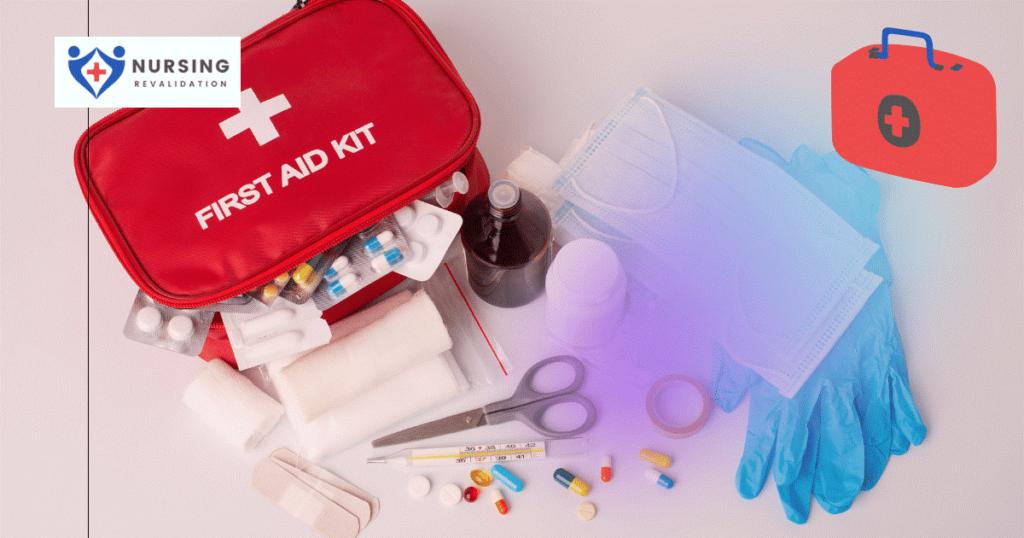
First aid kit:
Staying prepared requires having a kit in your house, car, and place of business. The following items are commonly found in a first-aid kit:
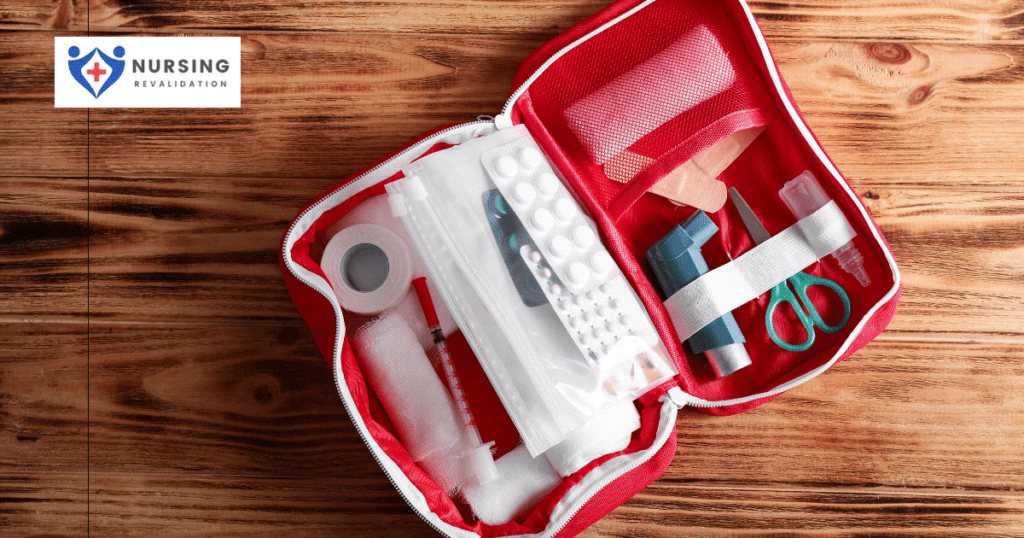 Bandages, roller bandages, and tape
Bandages, roller bandages, and tape- Sterile gauze
- Chemical cold pack
- Antibiotic cream
- Antiseptic wipes and swabs
- Burn ointment
- Absorbent compresses
- First aid reference guide that includes local phone numbers
- Mask for breathing (rescue breathing/CPR)
- Eye shield and eyewash
Nursing revalidation provides interactive courses for first aid certification. Join the course and start providing basic life support to others.

